Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act of Nepal
30 September 2019
1) Background
Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act, 2019 (“FITTA“) has replaced the previous Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act, 1992. The aim of FITTA is to reform the existing legal framework of foreign investment in Nepal to facilitate new investments. This article provides general information on the new provisions introduced by FITTA in comparison to the previous one.
2) Scope of FITTA
FITTA which governs foreign investment and technology transfer has wider scope than the previous one. The definition of a foreign investor now includes Non-Resident Nepali (“NRN“) alongside foreign individual, firm, organization and government.
Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act, 1992, covered the following as foreign investment:
a) Investment in share (Equity);
b) Re-investments of the earnings derived from the investment; and
c) Investment made in form of loan or loan facilities as investment.
FITTA has removed loan investment under the definition of foreign investment and is treated separately as project loan. FITTA considers the following as foreign investment:
(a) Investment in shares in foreign currency;
(b) Re-investment of the profits earned from foreign currency or shares;
(c) Investment through lease of airlines, ships, machinery;
(d) Investment in venture capital fund;
(e) Investment in secondary stock market;
(f) Investment by issuing securities in foreign stock markets
(g) Investment done by purchasing shares or assets of company established in Nepal;
(h) Technology transfer (licensing of foreign intellectual property, franchising, management, technical and marketing services) ; and
(i) Investment done by establishment and expansion of industry in Nepal.
3) Technology Transfer
- Subject of technology transfer
Patent, design, trademark, goodwill, technological specialization, formula, procedure, user’s license, know-how sharing, franchise, technical and management and advertising services come under the scope of technology transfer.
2. Approval
Technology transfer agreement must be approved from the Department of Industry and technology transfer is allowed even in areas where foreign investment is restricted.
3. Royalty
The royalties and fees pursuant to the technology transfer agreements can be repatriated after the approval of the Department of Industry.
4) Minimum Investment Amount
Pursuant to the notice of the Ministry of Industry, Commerce and Supplies dated 29 May 2019, a foreign investor is required to invest at least NPR 50 million (approx. USD 450,000).
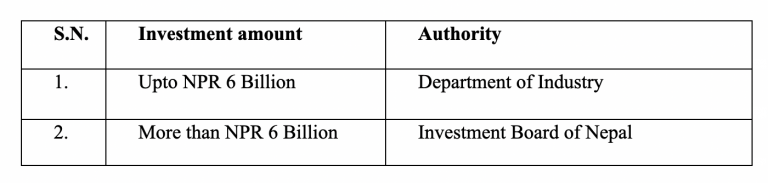
5) Approving Authority
The approving authority of foreign investment is determined by the amount of investment as set out below:
6) Visa Facilities
Following facilities related to visa will be provided for the foreign investor:
- Foreigners willing to come Nepal for study, research or survey for investment will be provided with 6 months non-tourist visa.
- Investor or one authorized representative of the investor and his/her family members will be provided with business visa for investment made up to the minimum investment amount.
- For investors investing more than the fixed minimum investment amount, business visa is provided to maximum of two person and their family members.
- For investors investing more than USD 1 million at a time, such investor or representative and their family will be provided with residential visa.
- Foreign specialist, technician or managerial staff will be provided with non-tourist visa.
Foreign technician and managerial staffs can be enrolled in company if those kind of manpower is not available in Nepal upon obtaining work permit.
7) One-Stop Service Mechanism
FITTA has incorporated new provision of one-stop service mechanism which was not included in previous provision to provide exemptions, facilities, concession or services to foreign investor through single service mechanism. One-stop Service Centre has recently been established within the premises of the Department of Industry for the facilitation of foreign investment.
8) Repatriation
FITTA enables foreign investors to repatriate all forms of investment as per the law after clearing all applicable taxes. FITTA permits to repatriate profits, benefits, income, proceeds of sale of shares. Foreign investors should confirm that they have followed “laws, agreements and obligations” so as to be permitted to repatriate. Investors can repatriate the amount of investment in the same currency of investment or in other convertible foreign currency with approval of Nepal Rastra Bank.
9) Dispute settlement mechanism
In case of dispute between a foreign investor and Nepalese nationals, disputes should be settled by mutual discussions or negotiations. If the disputes can not be settled by mutual discussions or negotiations within 45 days of arising of the disputes, such must be resolved as per the joint investment agreement or through dispute resolution agreement if any.
The Department of Industry/Investment Board must be informed within 15 days of settlement of dispute. If the dispute cannot be resolved even after taking the afore mentioned measures, the dispute must be resolved in accordance to the prevailing arbitration laws of Nepal.
10) Permitted and restricted areas for investment
Investments can be done only in sectors that are classified as industries by the Industrial Enterprises Act 2016 and not restricted by FIITA.
The following sectors are restricted by FITTA for foreign investment:
- Animal husbandry, pisciculture, beekeeping, fruits, vegetables, oilseeds, dairy products and other primary sectors of agriculture;
- Cottage industries;
- Personal service related business such as tailoring, driving, barber shop;
- Arms and ammunition industry that manufactures arms and ammunitions, explosives, nuclear biological and chemical weapons, atomic energy and radio-active materials;
- Buying and selling of the real estate other than construction of houses, remittance service;
- Travel agency, tour guides, trekking and mountaineering guides, rural tourism such as home stay;
- Mass-media business such as newspapers, radio, TV and online news, national language movies;
- Management, accounting, engineering, legal consultation services and language training, music training, computer training; and
- Any other consulting services having more than 51% of foreign investment.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and shall not be construed as legal advice, advertisement, personal communication, solicitation or inducement of any sort from the firm or any of its members. The firm shall not be liable for consequences arising out of any action undertaken by any person relying on the information provided herein.



