Arbitration Law in Nepal: Arbitration Lawyers in Nepal
28 May 2020
(Arbitration Lawyers/Law Firm in Nepal)
This article highlights the legal provision on the Arbitration Act, 1999 (2055) (the " Arbitration Act") of Nepal.
1) Background
The main law governing arbitration in Nepal is the Arbitration Act and Arbitration Rules, 2059 (the “Arbitration Rules”). The Arbitration Act was introduced repealing the Arbitration Act, 1981 (2038).
The Arbitration Act incorporates the detailed procedure for settlement of the dispute through arbitration in Nepal.
2) Dispute settlement through arbitration
If the agreement comprises a detail procedure of the settlement of disputes through arbitration then the dispute should be settled pursuant to the agreement. In absence of any procedure mentioned in the agreement, the dispute should be settled as the procedure outline in the Arbitration Act.
Further cases of civil suit related to commercial nature can be settled through the arbitration by mutual consent of parties.
3) Number of arbitrators

Please Note: If the number of appointed arbitrators under the agreement is even then the number should be turned into an odd by appointing an additional arbitrator by existing arbitrators.
4) Appointment of the arbitrator:
The process of appointment of arbitrators must be started within 3 months from the date when the reason for the settlement of a dispute through arbitration arises.
Party of the agreement will respectively appoint one arbitrator each and the appointed arbitrators should appoint the third arbitrator who should work as the chief arbitrator.
In case the agreement has incorporated the separate provision of appointment of arbitrators, an appointment should be done as mentioned in the agreement.
5) Appointment of arbitrator through the court:
If parties fail to appoint an arbitrator as mentioned in arbitration agreement or agreements fails to incorporate the provision of arbitration then an application can be submitted to the high court along with a copy of the agreement and details of minimum three persons who are to be appointed as arbitrator.
If parties fail to make consensus on the proposed name of the arbitrator, the high court will appoint a qualified arbitrator within 60 days from the date of receiving the application. The decision taken by the court is final.
6) Qualification of arbitration
The following person is not qualified for appointment as an arbitrator;

7) Removal of arbitrator
If parties intend to remove the arbitrator then they can remove the arbitrator as per the provision mentioned in the agreement.
If the agreement is silent regarding the removable of arbitrator parties can remove the arbitrator in the following conditions:
- In case any arbitrator is clearly seen as bias or discriminated against any party instead of working in an impartial manner,
- Any arbitrator engages in improper conduct or commits fraud in the course of arbitration,
- Frequently commits mistakes or irregularities in the course of arbitration,
- Does not attend arbitration meetings or refuses to take part in arbitration proceedings for more than three times without furnishing satisfactory reasons with the objective of prolonging or delaying the arbitration proceedings in an improper manner,
- Takes any action which is opposed to the principles or rules of natural justice,
- The Arbitrator is found to be lacking the necessary qualifications or to have ceased to be qualified.
8) Place of arbitration
The place of arbitration should be as specified in the agreement. If the agreement does not specify a place of arbitration then:
- The Place of arbitration should be determined by the concerned parties.
- In case the concerned parties are unable to select a place within 15 days from the date of appointment of the arbitrator or in case the concerned parties fail to reach an agreement then the place should be as specified by the arbitrator.
9) Language to be used in arbitration:
Language to be used in arbitration should be as specified by the agreement. If agreements fail to specify the language then it should be determined by the parties of agreement in consent.
If parties are unable to reach consent then the language used in the agreement should be used during the arbitration proceeding.
10) Arbitration proceeding
The procedure of settlement of dispute relating to arbitration includes the following steps:
10.1. Submission of claims
Plaintiff should submit its claim before the arbitrator in writing along with evidence. The Claim should be submitted within the following timeline:
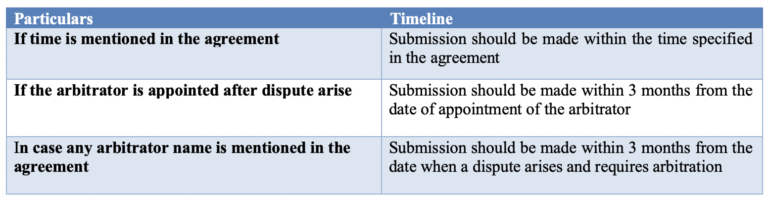
10.2. Counter-claim
If time is mentioned in the agreement the opponent party should submit its objection within the timeline mentioned in the agreement. If such provision has not been incorporated then counterclaims should be made within 30 days from the date of receipt of the claim.
10.3. Rejoinders
The rejoinders should be submitted within 15 days from the date of submission of the counter claim. A copy of the rejoinder should also be provided to the opponent party.
10.4. Extension of submission time
In case any party fails to submit its counterclaim or rejoinder within the time limit due to circumstances beyond the control of the party, the party can submit an application to the arbitrator for an extension of the time limit within 15 days from the date of expiry of the time limit.
If the reason for the extensions seems satisfactory the arbitrator may extend the time limit as requested.
11) Power of Arbitrator
The arbitrator can exercise following power during the decision-making process:
- To direct the concerned parties to appear before an arbitrator to submit documents, and record their statements as required,
- To record statements of the witness,
- To appoint an expert and seek their opinion or cause examination on any specific issue,
- Obtain the bank guarantee or any appropriate guarantee for foreign nationals,
- To inspect the place, object, product, structure, production process or any other related matter which are connected with the dispute,
- Sell the material or object which is likely to be destroyed or damaged after consultation with the parties,
- To exercise any specific power conferred by the parties,
- To issue preliminary orders, or interim or inter locating orders in respect to any matter connected with the dispute on the request of any party, or make a conditional decision and
- To issue a certified copy of the document
12) The Decision of Arbitration:
Except otherwise provided in the agreement, the arbitrator should pronounce the decision within 120 days from the date of submission of claim documents. In case there are three or more arbitrators, the decision of the majority prevails.
13) Ground for challenging the decision of the arbitration
Any party who is not satisfied with the decision of the arbitrator can file a petition before the high court within 35 days from the date of decision heard or notice received.
13.1. High court may invalidate the decision or give an order to issue a fresh decision on the following grounds:
- In case any party to the agreement was incompetent for any reason to sign the agreement at the time of signing the agreement or in case the agreement is not valid under the law of the nation which governs jurisdiction over the parties or in case such law is not clear and agreement is not valid under the laws of Nepal,
- Ifnotice to appoint an arbitrator or notice regarding the arbitration proceedings is not given to opponent,
- In case the decision has been taken on the disputed matter which had not been referred to the arbitrator or in a manner contrary to the conditions prescribed for the arbitrator or by acting beyond the jurisdiction prescribed for the arbitrator or
- In case the procedure of decision making of arbitration is against the procedure prescribed by the agreement or against the procedure prescribed by the arbitrating act.
13.2. Appellate Court can invalidate the decision of the arbitrator in the following grounds:
- In case the dispute settled by the arbitrator cannot be settled through arbitration under the laws of Nepal.
- In case the decision taken by the arbitrator is likely to be against the public interests or policies of Nepal
14) Implementation of the decision of the arbitration
The party of the agreement should implement the award within 45 days from the date when the party receives a copy of the award. In case an award is not implemented, the concerned party should file an application before the district court within 30 days from the date of expiry of the time limit. The district court should implements the award within 30 days as its own judgment.
15) Implementation of award taken in a Foreign Country:
A party willing to implement an award made in a foreign country in Nepal should submit an application to the High Court along with the following documents:
- The original or certified copy of the arbitrator’s award.
- The original or certified copy of the agreement.
- In case the arbitrator’s award is not in the Nepali Language, an official translation thereof in the Nepali language.
The following conditions should be satisfied for the Foreign Arbitral Award to be enforced in Nepal:
- The appointment of the arbitrator and award should have been made in accordance with the processes agreed in the agreement entered between the parties,
- The parties to the dispute should have been duly notified as to the proceedings of the arbitration,
- The award should be rendered only on the matter strictly entrusted to the arbitrator and in accordance with the provisions of the agreement,
- The award should have become final and binding upon the parties as per the laws of the jurisdiction in which such award was rendered,
- The laws of the country of the applicant or the laws of the country where such arbitration award was rendered should not prevent the recognition and enforcement of any arbitral award given in Nepal,
- The application for the enforcement of an arbitral award should have been filed before the court of Nepal within 90 days from the date of the arbitral award.
However, under the following circumstances the foreign award cannot be enforced in Nepal:
- In case the awarded settled dispute cannot be settled through arbitration under the laws of Nepal.
- In case the implementation of the award is detrimental to the public policy.
If the high court is satisfied that the award has to be enforced in Nepal, it should forward the award to the district court for its implementations.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and shall not be construed as legal advice, advertisement, personal communication, solicitation or inducement of any sort from the firm or any of its members. The firm shall not be liable for consequences arising out of any action undertaken by any person relying on the information provided herein.
Related Professionals
aaa



